Virtually Amazing: What to Know about Augmented Reality (AR) for eLearning
If augmented reality (AR) was a once prediction of a few futurists, that’s not the case anymore. Nowadays, AR technology has real applications in real-world contexts—and eLearning is one of those contexts. So today, we’ll talk about augmented reality in eLearning.
It might sound like an inaccessible innovation for many of us, but 1.5 billion consumers are using AR worldwide. Plus, the mobile devices with cameras we use every day support AR.
Let’s find out how AR in eLearning raises the interaction and effectiveness of your training programs.
What Is Augmented Reality?
AR is a technology, but it’s also an experience. Take your surroundings, mix them with a computer-generated environment, et voilà! You’re in an AR environment provided by an AR app.
Then, when you start interacting with the AR environment, it reacts to your actions. As a result, you get real-time information tied to your surroundings. And that information adds to your surroundings in myriad ways.
For instance, you might use AR when messaging through social apps, gaming, or shopping. And you might use your smartphone or tablet to do it, but AR glasses might soon become popular AR gadgets.
An example of a real-world context where you could use an AR app is house hunting. You could walk down a street, hold up your camera, and see on your smartphone’s screen which houses are for sale and their selling price.

To give you an example of interactive learning with augmented reality, picture a textbook. A pair of smart glasses with object recognition capabilities would scan the book while you’re reading it. Then, the glasses would display definitions, stats, or videos on the side of the book to help you understand certain concepts.
Next, we’ll describe a few examples of how you can use augmented reality in eLearning contexts.
Examples of AR in eLearning
Here’s a collection of scenarios and industries in which you can use augmented reality in eLearning:
1. Safety Training
If you provide your staff with an eLearning course on office safety, you might spice up the experience for them. All you have to do is deliver the course on a mobile eLearning app that supports AR.
Then, while listening to an audio or watching a video of an instructor speaking on the app, your employees could hold up their smartphone, point it around the office, and the app would display the evacuation path they should follow.
2. Employee Onboarding
Another example of interactive learning with augmented reality might be employee onboarding. When a new hire arrives at the office, locating the place where each person sits might be challenging.
If they wore a pair of smart glasses, they could simply indicate the name of the person they were looking for (by voice or gestures) and follow the glasses’ instructions. Those instructions could combine audio played by the glasses and images displayed on the lenses. Then, the new hire would walk around the office and wait for the glasses’ facial recognition capabilities to kick in.
3. Medical Training
AR can satisfy the requirements of training medical, paramedical, and nursing students and staff. The smart glasses market is expected to grow about $69 million over the period of 2021–2025. This means that AR-enabled hardware and software will be more available and likely affordable.
By overlaying a real-world setting with virtual information, AR eLearning teaches to diagnose. It also teaches how to determine the best course of treatment.
For instance, adding images of injuries to patient models helps nursing students build their diagnosis skills. AR shows these students that each decision leads to a specific outcome. This way, they get to see the (simulated) consequences of their actions.
Another area in which augmented reality in eLearning can help is psychiatry. Aspiring psychiatrists can experience the simulation of hallucinations over their surroundings. These healthcare professionals can learn what it feels like to have hallucinations. Consequently, they’ll empathize with their patients more and give them better treatment.
Lastly, AR can also help train doctors, nurses, and other ER staff to operate in crisis scenarios. For instance, it can tell them how to manage an unusual incoming patient flow—how to prioritize patients based on severity and where to send them.
4. Engineering Training
AR applies to engineering training too. It helps engineering learners—in many different industries—identify and understand complex systems and structures.
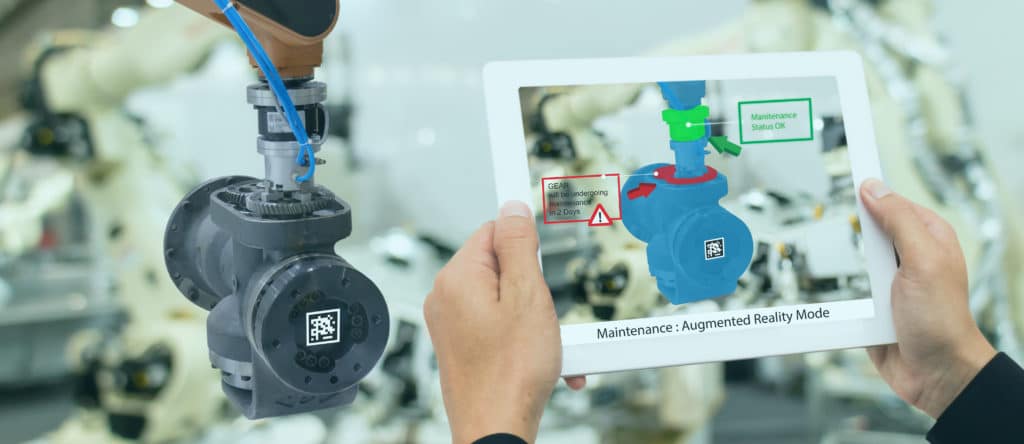

And one of those industries is mechanics. With AR simulations, mechanics in training can learn where each part is, what it does, and how it integrates with others. As a result, these learners understand better how mechanical systems work.
The same goes for industrial workers who operate production machines. Using AR simulations to learn how to perform their jobs prevents workplace accidents and injuries.
An AR simulation overlays what the user is actually seeing around them with helpful information. The user interacts with the real world—in real-time—while AR adds virtual elements to the scenario. Those virtual elements can be text, links, photos, 2D illustrations, virtual 3D objects, audio clips, or videos.
These added elements relate to the learners’ actual surroundings. Sometimes, they’re interactive and react to gesture or voice commands or the user can move them according to task instructions.
Another engineering learning context to which AR applies is construction. Crane and other machine operators can learn to better handle their machines with AR. Other construction workers can also benefit from AR when learning to use their tools and equipment.
The technology adds guiding information in real-time to what they see while doing their jobs. And in the case of machine operators, learning effectiveness raises as they learn while experiencing the stress of handling their machines in real life.
5. Sales Training
Serious games are entertaining—that’s why they’re games—but they’re also educational. Because they’re both fun and educational, they’re engaging and effective, making them outstanding training tools.
Remember Pokémon Go? It’s the perfect example of AR. Now, imagine you could use fictional customers played by animated characters in a real-world scenario to train your sales personnel. Well, with AR in corporate training, you can!

While standing behind a store counter, a sales rep could wear a pair of smart glasses and use an AR app to learn to handle an angry customer. And the app could use elements of gamification to make the learning experience more engaging. For instance, at an advanced level, if you prevented the fictional customer from filing a complaint, you’d earn points towards a badge.
6. Language Learning
AR suits the needs of learning a new language while moving around the house, office, or anywhere else. For instance, while walking around a supermarket, you can learn new vocabulary. You can also practice oral or written conversation in a new language with a virtual language teacher while traveling on a train.
In the corporate world, a language-learning AR app can train a global workforce in many different ways.
- By placing virtual elements—such as labels or audio clips—next to real-world objects, using object recognition
- By displaying animals, objects, and other things in the surroundings with corresponding labels and audio clips attached
- By simulating real-life conversations with animated characters that interact with you via chatbot technology and speech recognition
Labels and audio clips teach the foreign language word for each physical object. On the other hand, chatbot conversations allow practicing pronunciation and fluency on various topics.
With AR, language learning apps enable learners to discover new words and sentences while exploring their surroundings. Additionally, an artificially-intelligent virtual language teacher understands and answers what a learner says and gives them feedback on pronunciation.
Now, let’s talk about perks.
Why Use AR in eLearning? 7 Key Benefits
AR apps are usually more expensive than non-AR apps as they require more development time and expertise. For instance, they need software developers to implement AR scanners (or buy off-the-shelf ones).
However, using augmented reality in eLearning definitely pays off. AR apps are worth the investment as they improve the effectiveness of your elearning programs.
1. Retention
By adding information to your learners’ surroundings, an AR app offers them an interactive learning experience. This translates to higher levels of knowledge retention.
For instance, an AR app might add links, photos, or videos to a learner’s surroundings at work to build a scenario. It might also allow the learner to adopt an avatar and play a role in that scenario. In turn, the scenario would react to the role-playing. And that’s an approach to AR in corporate training that promotes knowledge retention.
2. Recall
Another benefit of augmented reality in learning has to do with knowledge recall. An AR app might reduce the need for endless reading and memorizing processes and procedures.
For instance, your staff might just grab their smartphones or a pair of smart glasses, point or look at the object they need to work with, and follow the instructions that the device adds to their surroundings. This means that your workforce will learn on demand and on the job.

3. Comprehension
It is much easier to visualize complex concepts and objects by using augmented reality in learning. Reading or listening to an online instructor doesn’t always allow the learner to understand the topic.
Think of the human body, a motor, a heavy machine, a vehicle, a molecule, or another complex concept or system. Absorbing, retaining, and recalling the structure and behavior is much more difficult without AR.
This kind of technology allows the inspection of those systems in ways that reality doesn’t allow. For instance, you can’t zoom in on the internal parts of a heart in real life. And a plastic model is not as realistic as its 3D representation.
4. Engagement
AR fosters active learning. In other words, learners interact with content and, in some cases, practice new skills right away, in real-time. They take action instead of only observing. This way, it’s easier to explain, understand, and remember new concepts and procedures.
Consequently, learners become highly motivated, engage more with the learning process, and focus more on the learning content.
Also, AR apps put the learner in a new setting—their surroundings combined with the AR environment. And that’s exciting! But there’s more…
Engaging technologies such as augmented reality in eLearning boost the learner’s curiosity and creativity. This improves problem-solving skills.
By using AR in corporate training, thus achieving higher levels of engagement, you raise your staff’s satisfaction. As a consequence, you reduce employee turnover and, because news travels fast, you attract the best talent.
5. Effectiveness and Efficiency
Learning with a less traditional technology such as AR is highly effective. Not only do you attain the learning outcomes you defined for your elearning course, but you also get higher course completion rates.
In addition, augmented reality in eLearning saves learners a lot of time by answering their questions. Here’s an example: A high-quality virtual 3D car embedded in an AR app versus the car’s manual or a traditional online course that would teach all the car’s features with written content, photos, illustrations, and videos. Sales reps could explore the virtual car would probably and may have fewer remaining questions by the end of the course. And that would save the time of instructors, peers, or managers answering those questions.
6. Mobility
Imagine onboarding an employee to work at a logistics warehouse. You’d have to show them the warehouse’s areas and how packets move around the infrastructure.
Of course, they could sit in an office and read a paper or PDF training manual with pictures. You could even give them a tour around the warehouse, point at the areas, and describe how packets move around.
Nevertheless, neither a manual nor tour would give your new hire the learning experience an AR app could. It’s easier to visualize the warehouse’s areas and understand how the facilities function with AR.
Your employee could point their smartphone or tablet around the warehouse and learn how it works. The AR app would recognize each area and add text, audio clips, and even animations to the screen.
7. Safety and Cost
AR allows learners to practice new skills without the risks of doing so in real life. And healthcare is one of the sectors that use augmented reality in learning.
For instance, nursing students can learn through simulated images of injuries with an AR app over human models. At Yale School of Nursing, a team developed such an app.
It works with a smartphone or tablet, paper-printed QR codes, and CPR manikins or someone’s body. The nursing student holds the smartphone or tablet over a QR code on the manikin or person.
Then, the AR app renders an image of the injury and displays it on the QR code. And that’s when the learning starts! The aspiring nurse runs through a set of questions to diagnose and figure out the best treatment for the injury.
Another app the team at Yale School of Nursing developed simulates visual and auditory hallucinations. The app allows nursing students to understand better how their patients feel when hallucinating. This means that the app trains health practitioners to empathize with their patients. And it enables these students to get closer to practice than they would if they studied through a textbook.
Both the injury simulation and hallucinations apps are safe and low-cost healthcare training solutions. It’s impossible to hurt a manikin. And for Yale’s injury simulation app, you only need a CPR chest dummy that costs a few hundred dollars.
And as for the hallucinations app, an AR headset is not that cheap—roughly $3,000. But a smartphone or a tablet is less expensive.
Healthcare is not the only industry that spends loads of money on training equipment. Aviation, military, law enforcement, firefighting, or aerospace can save significant amounts of money training their staff with AR. For instance, with an AR app, airplane pilots can learn where each dashboard component is.
At this point, you already know what AR in eLearning is and what it can do for your corporate training. So it’s time to learn how it might come to life in your eLearning programs.
How to Implement Augmented Reality In Your eLearning Programs
Here’s what we suggest you do to create an AR app and start delivering your online training courses through it:
1. Gather the Right Professionals
To incorporate AR in an eLearning app, you need one of the following:
- A full-stack software developer who specialized in AR implementations
If you have a tight budget, you might go straight to option number one. However, in that case, make sure that the full-stack developer implements solutions according to UX/UI guidelines.
The developer will code the functioning and visual interface of your AR eLearning app. Whoever does it, UX/UI design concerns the interface’s structure, look and feel, and ways to interact with the app. The goal is to come up with an app that’s visually appealing, easy to use, and aligned with your needs.
If you have the budget, you should also consider hiring a quality assurance (QA) specialist. They’ll make sure that the app works and looks as expected. If you don’t have the budget, ensure that the developer incorporates QA practices in their development process.
Besides the developer, UX/UI designer, and QA specialist, you need the other roles of eLearning project development. That’s a project manager, a learning experience designer (LXD), a scriptwriter, an illustrator, and a voice-over artist. You might also need a 3D artist to do 3D modeling and rendering.
2. Move Slowly Yet Steadily
Because developing an AR eLearning app is a tough job, we recommend working incrementally. This means building increasingly complex versions of the app. You can start with a minimum viable product (MVP)—a version of the app containing only essential features.
It may look sketchy and won’t do everything that it will eventually do, but it’s a great starting point. And it minimizes the expenses you could face if you waited until the end of the project to check if the app fulfills the requirements.
3. Involve the Learner in the Process
Developing an AR eLearning app with the learners’ involvement is highly important. Their impression of the app is one of the most crucial factors of the course’s success.
Therefore, you should ask your learners to try the app and give feedback on how easy it is to use it. The sooner you do that, the better. Each time you call the learners in, their app evaluation might get the final app closer to your expectations.
4. Participate in the Process
Whether you develop your AR eLearning app in-house, hire an eLearning agency to do it, or work with a team of freelancers, you should participate in the process. That’ll increase the odds of getting better learning outcomes down the line.
The reason? You know your learners, organization, goals, and business best. And if you’re an expert in the course’s topic, you know more about the subject matter than the project team.
You should share that knowledge with the team and be available to answer all their questions. Participate in at least the most needle-moving meetings to assess progress and adjust the process accordingly.
Some Final Considerations and a Checklist
How do you know if your AR eLearning app is up for the challenge? This is the checklist you might use to figure it out for yourself:
- It’s highly interactive. Instead of moving through the course one screen at a time, an AR eLearning app allows your staff to learn by interacting with the AR environment. This includes looking up information and reading it, manipulating virtual objects, listening to audio clips, or watching videos.
- It’s highly realistic. This means virtual objects seem real and respond realistically when learners interact with them. It also means that the AR developer rendered those objects at a high frame rate that’s still high-performing.
- It delivers a strategic learning experience. The AR eLearning app’s success doesn’t depend solely on the technology and the devices. The learning experience designer must still determine the best strategy to reach the learning outcomes.
Finally, as to the options on the table for building the project team, let us give you our perspective.
- In-house team — demands for experience in software and AR development and a budget for social and fiscal obligations with staff
- Freelancers — requires that you allocate internal resources to manage their work, plus they could leave the project anytime
If you choose to proceed with the eLearning agency option, give us a call or drop us a line! We would be delighted to help you put all the pieces together and make your project of augmented reality in eLearning come true.
The post Virtually Amazing: What to Know about Augmented Reality (AR) for eLearning appeared first on ELM Learning.
This content was originally published here.


